Elliptic Curve Cryptography
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is a public-key encryption algorithm based on the mathematics of elliptic curves.
The main advantage of ECC is that it uses shorter key lengths compared to the RSA encryption algorithm while providing an equivalent level of security. Another advantage of ECC is its ability to define bilinear pairings between groups, based on the Weil pairing or Tate pairing; bilinear pairings have found numerous applications in cryptography, such as identity-based encryption (IBE).
ECC can achieve a security level equivalent to that of RSA with much longer keys by using shorter keys, making it widely adopted in protocols like HTTPS, SSH, and PGP, as well as on blockchains such as Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH).
Theory
Elliptic curves for cryptographic applications are plane curves defined over a finite field (not the real number field), with the following equation:
There is a special point at infinity (denoted as ∞). The coordinates are chosen from a specific finite field with characteristic not equal to 2 or 3, and more complex curve equations may also be used.
The set generated by an elliptic curve forms an Abelian group, with the point at infinity as the identity element. The structure of this group inherits the structure of divisors in the following algebraic variety:
Working Principle
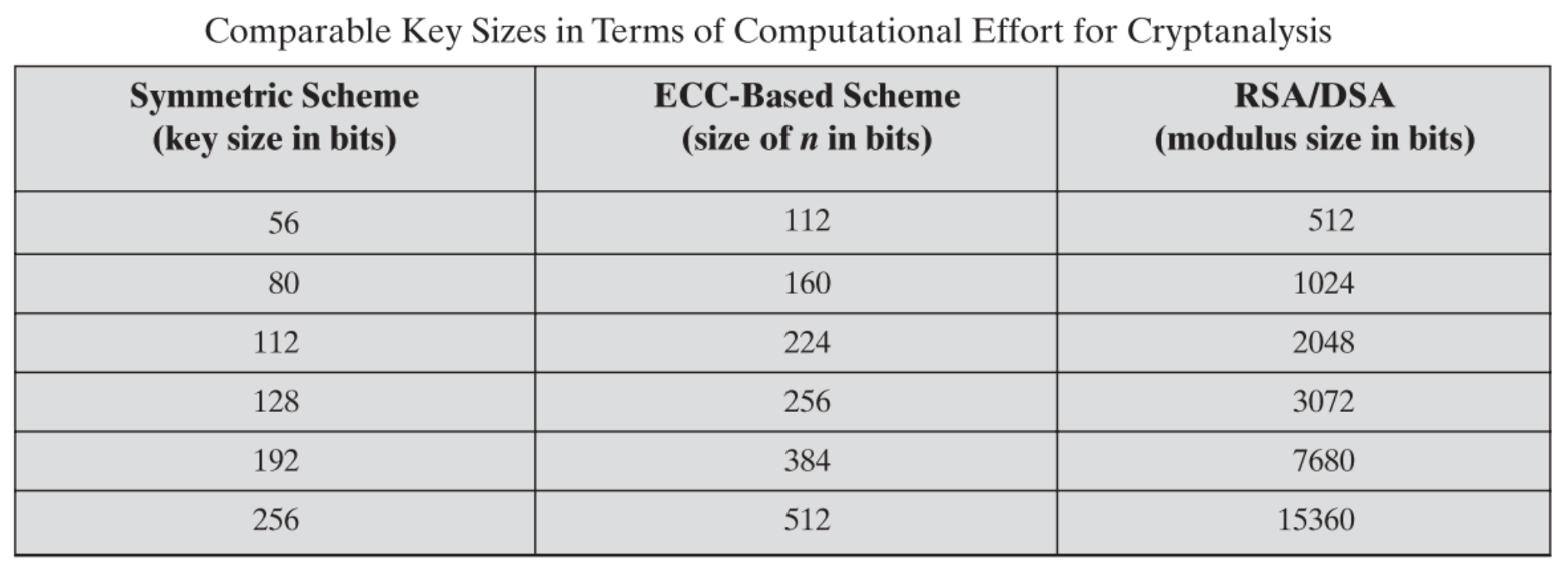
ECC is based on another advanced mathematical field called elliptic curves. An elliptic curve is a curve described by the equation y2 = x3 + ax + b ,where a and b are constants, and the domain of the curve is a finite field. The graph is plotted as follows:
Elliptic curves possess unique properties that make them both interesting and practical for mathematicians and cryptographers. Firstly, elliptic curves exhibit horizontal symmetry—the parts on either side of the x-axis (horizontal axis) are identical, like a mirror image.
Additionally, any line not perpendicular to the elliptic curve intersects the curve at no more than three points. In the example below, these points are marked as P, Q, and R.
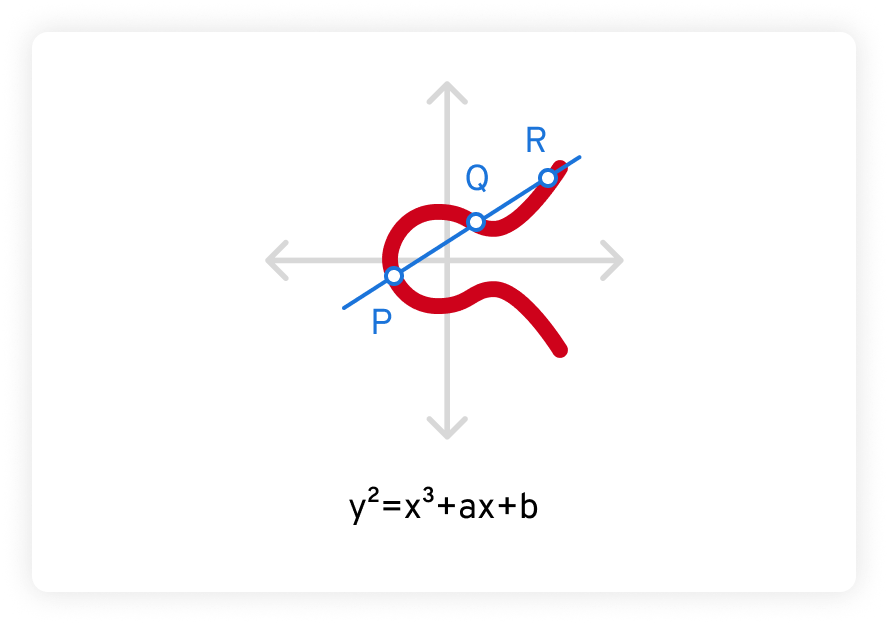
The security of elliptic curve encryption algorithms is based on the difficulty of solving the Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem (ECDLP). Given a point P on the curve and a scalar k, it is extremely difficult to determine a point Q such that Q = k*P —far more difficult than factoring an extremely large integer.
This characteristic means ECC can provide security equivalent to or even more reliable than RSA, while using key lengths significantly shorter than those required by RSA.
Key Construction and Signature Principles
Private Key: Randomly select an integer d ∈ [1, n−1];
Public Key: Q = d·G (where G is the base point of the elliptic curve);
Signature: Generate (r, s) by hashing the message and performing elliptic curve scalar multiplication using ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm);
Verification: Validate the signature’s authenticity using the public key Q.
Application of ECC in the DF Protocol
Encrypted Communication: Generate session-level shared keys based on ECDH to implement end-to-end AES-256 symmetric encryption;
Identity Authentication: Use ECC to construct a binding mechanism between Node DH-ID and on-chain signatures, ensuring the uniqueness and unforgeability of node identities;
Computing Power Reporting Signature: Each task is confirmed by a node signature, guaranteeing the on-chain verifiability and non-repudiation of computing power data.
Security and Performance Advantages
ECC offers an upgrade path for enhanced quantum resistance (e.g., SIDH) and boasts the following advantages:
256-bit keys achieve military-grade security;
Faster signature and decryption operations compared to RSA;
Compact asymmetric keys, facilitating on-chain storage and rapid verification;
High scalability, enabling combination with modules such as zero-knowledge proofs and threshold signatures.
Last updated